Kentwood, MI

How long does bone graft take to heal?
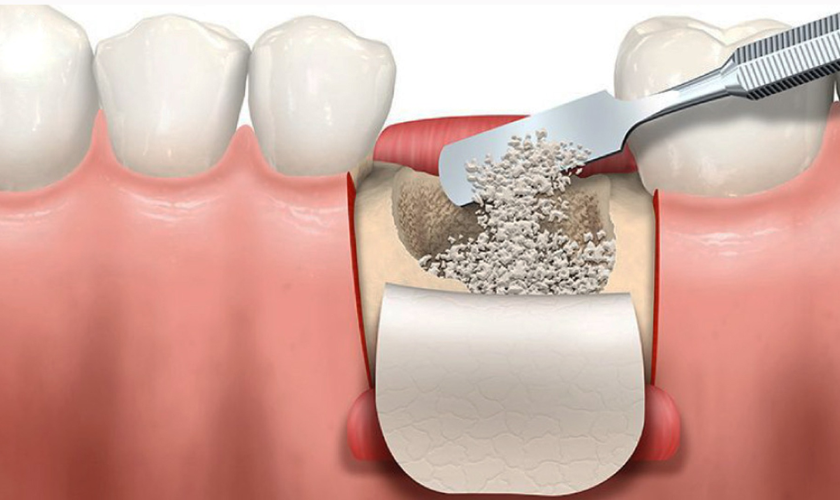
Bone grafting is a common procedure in dentistry and orthopedic surgery used to repair and rebuild bone that has been damaged or lost. Whether it’s due to injury, disease, or other factors, bone grafts play a crucial role in restoring function and aesthetics. If you’re considering or have recently undergone a bone graft, understanding the healing process can help manage expectations and ensure a successful outcome.
Understanding Bone Graft Healing
The healing of a bone graft typically occurs in several stages, each with its timeline and considerations:
Initial healing (0-2 weeks): Immediately after surgery, the focus is on initial healing and controlling pain and swelling. During this time, the body begins to form a blood clot at the graft site, which is essential for the healing process to begin.
Cellular Activity (2-8 weeks): Over the next few weeks, cellular Activity at the graft site increases. Specialized cells called osteoblasts start to produce a new bone matrix, which eventually replaces the graft material. This stage is crucial for the integration of the graft with the surrounding bone.
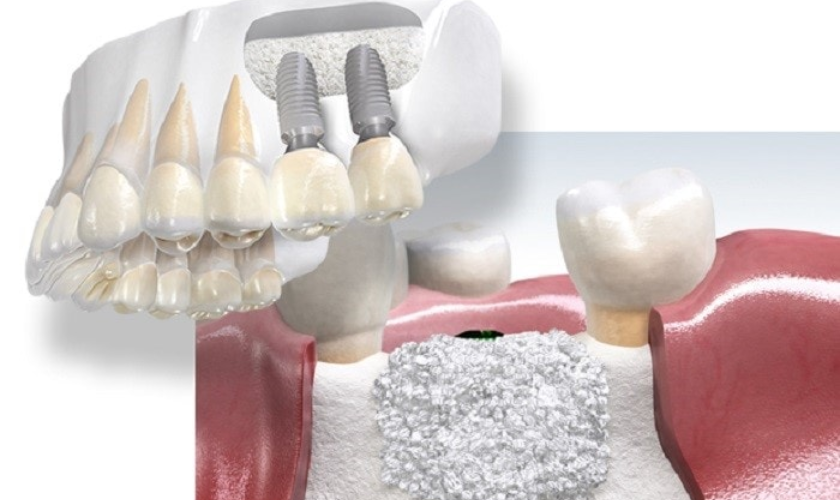
Bone Formation (8 weeks – 6 months): As the graft continues to heal, new bone formation becomes more evident. The graft material serves as a scaffold for new bone growth, gradually transforming into mature, functional bone. During this time, it’s important to follow your healthcare provider’s instructions for care and avoid activities that could disrupt the healing process.
Maturation (6 months – 1 year): The final stage of bone graft healing involves the maturation and remodeling of the newly formed bone. The bone undergoes structural changes to become stronger and more resilient, eventually blending seamlessly with the surrounding bone.
Factors Affecting Healing Time
Several factors can influence the healing time of a bone graft, including:
Graft Type
The type of graft material used can significantly impact healing time. Autografts, for instance, are harvested from the patient’s own body, such as from the hip or kaws. It heals faster than allografts that are acquired from a donor. Autografts contain living cells and growth factors that promote faster healing and integration with the surrounding bone.
Size and Shape
The size and shape of the graft can also affect healing time. Larger grafts may take longer to heal as they require more new bone formation to fill the graft site. Additionally, irregularly shaped grafts may take longer to integrate fully with the surrounding bone compared to more uniform shapes.
Patient Age
Age can impact the healing process, with younger patients generally experiencing faster healing than older patients. This is because younger individuals tend to have better blood circulation and higher levels of bone-forming cells, which are essential for the healing process.
Smoking

Smoking has been shown to impact bone healing negatively. Nicotine and other chemicals in cigarettes can reduce blood flow to the graft site. As a result, it impairs the delivery of oxygen and nutrients necessary for healing. Smokers may experience delayed healing and an increased risk of complications following bone graft surgery.
While the timeline for bone graft healing may vary depending on several factors, one thing remains constant. It’s the importance of proactive care and adherence to your healthcare provider’s instructions. As you progress through the healing process, celebrate each milestone, no matter how small, and remain committed to your recovery journey. Stay informed, ask questions, and lean on your healthcare team for support and guidance. So, embrace the journey, trust in your body’s innate healing power, and know that each day brings you one step closer to full recovery. Your commitment to your health and well-being today will pave the way for a brighter, healthier tomorrow. Here’s to your continued healing and a future filled with strength, resilience, and vitality.