Kentwood, MI

Why Choose White Fillings Over Traditional Amalgam?
When it comes to dental fillings, patients often find themselves choosing between traditional amalgam fillings and newer composite resin or white fillings. While both types serve the same primary purpose—repairing cavities and restoring teeth—there are significant differences between them.
This blog will explore the reasons why many people are opting for white fillings over traditional amalgams, focusing on aesthetics, health implications, durability, and more.
Amalgam or White Fillings: Differences Between These Two
Before diving into the benefits of white fillings, it’s essential to understand what each material consists of:
Amalgam Fillings
- Composition: Amalgam is a mixture of metals, including silver, mercury, tin, and copper. It is known for its durability and strength.
- Appearance: Amalgam fillings are metallic and dark, making them highly visible in the mouth.
- Durability: They are considered one of the most durable options for back teeth, often lasting 10 to 15 years or longer.
White Fillings (Composite Resin)
- Composition: White fillings are made from a mixture of plastic and fine glass particles, which can be tinted to match the natural color of your teeth.
- Appearance: These fillings are designed to blend seamlessly with your teeth, making them virtually invisible.
- Durability: While not as strong as amalgam, white fillings can last 5 to 10 years, depending on the location of the filling and how well you care for your teeth.
The Natural Look of White Fillings
One of the most significant advantages of white fillings is their aesthetic appeal. Here’s why aesthetics matter:
- Discreetness: Dentists can match white fillings to the color of your natural teeth, making them an excellent choice for visible areas in the mouth, such as the front teeth.
- Confidence Boost: Many patients report feeling more confident in their smiles after opting for white fillings, particularly those concerned about the appearance of amalgam.
- Customization: Dentists can tailor the shade of white fillings to ensure a perfect match with your natural tooth color, providing a seamless look.
Health Implications: Safety Concerns with Amalgam
While choosing between white fillings and amalgam, you should consider the health implications associated with each material.
Mercury Content In Amalgam
- Mercury Exposure: Amalgam fillings contain mercury, which can raise health concerns for some patients. While the American Dental Association (ADA) asserts that amalgam is safe for most people, those with certain allergies or sensitivities may prefer to avoid it.
- Environmental Concerns: The disposal of amalgam can also pose environmental risks, as mercury can be harmful to aquatic life.
Composite Resin Safety
- BPA-Free Options: Many manufacturers create modern composite fillings from BPA-free materials, reducing concerns about harmful chemicals.
- Fewer Allergens: Patients with metal allergies or sensitivities can find white fillings a more suitable option, as they are less likely to trigger allergic reactions.
Durability and Longevity: Choosing The Right Material
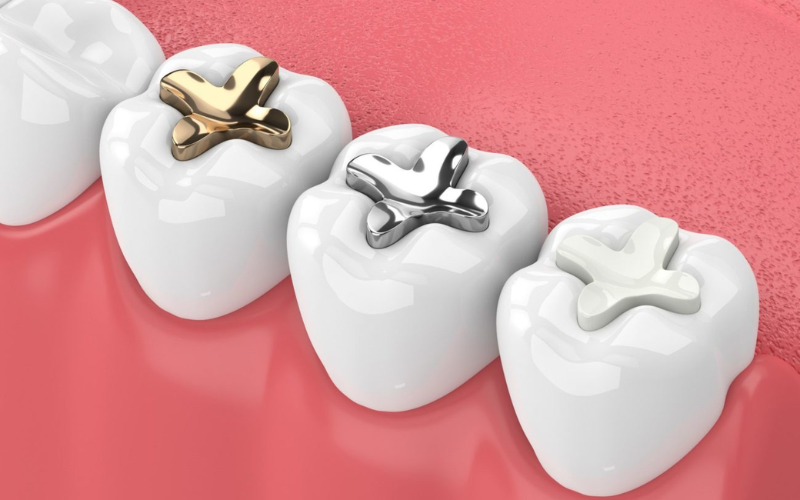
While both types of fillings serve their purpose, understanding their durability is essential for long-term dental health.
Amalgam Durability
- Strength: Dentists know that amalgam is strong, making it ideal for filling cavities in the back teeth, where biting forces are greatest.
- Longevity: With proper care, amalgam fillings can last over a decade, making them a popular choice for many dentists.
White Filling Durability
- Bite Force: While composite resin is durable, it may not withstand heavy biting forces as well as amalgam, particularly in the back teeth.
- Advancements: Recent advancements in composite materials have improved their strength and longevity, making them a more reliable option than in the past.
The Procedure: How Each Filling Is Placed?
The placement procedure for both types of fillings differs slightly, impacting the overall experience for the patient.
Amalgam Filling Procedure
- Numbing: The dentist numbs the area around the tooth to minimize discomfort.
- Cavity Removal: The dentist removes the decayed portion of the tooth using a drill.
- Filling Placement: The dentist mixes the amalgam, packs it into the cavity, and then shapes it to match the natural contours of the tooth.
- Curing: The filling hardens as it cools on its own without light curing.
White Filling Procedure
- Numbing: Similar to the amalgam process, the dentist numbs the area.
- Cavity Removal: The dentist removes the decayed tooth material.
- Layering: The dentist applies the composite resin in layers, curing each layer with a special light to harden it.
- Final Shaping: Once the dentist places all the layers, they shape the filling to fit the tooth perfectly.
Make The Right Choice for Your Dental Health!
Choosing between white fillings and traditional amalgam is a personal decision that depends on various factors, including aesthetics, health concerns, durability, and your specific dental needs.
While amalgam fillings have their advantages in terms of strength and longevity, white fillings offer a more natural appearance and fewer health risks.
If you’re considering dental fillings, consult your dentist to discuss which option is best for your situation. The choice ultimately comes down to what matters most to you—whether that’s the appearance, safety, or durability of your dental fillings.



